Processors for Embedded Vision
THIS TECHNOLOGY CATEGORY INCLUDES ANY DEVICE THAT EXECUTES VISION ALGORITHMS OR VISION SYSTEM CONTROL SOFTWARE
This technology category includes any device that executes vision algorithms or vision system control software. The following diagram shows a typical computer vision pipeline; processors are often optimized for the compute-intensive portions of the software workload.

The following examples represent distinctly different types of processor architectures for embedded vision, and each has advantages and trade-offs that depend on the workload. For this reason, many devices combine multiple processor types into a heterogeneous computing environment, often integrated into a single semiconductor component. In addition, a processor can be accelerated by dedicated hardware that improves performance on computer vision algorithms.
General-purpose CPUs
While computer vision algorithms can run on most general-purpose CPUs, desktop processors may not meet the design constraints of some systems. However, x86 processors and system boards can leverage the PC infrastructure for low-cost hardware and broadly-supported software development tools. Several Alliance Member companies also offer devices that integrate a RISC CPU core. A general-purpose CPU is best suited for heuristics, complex decision-making, network access, user interface, storage management, and overall control. A general purpose CPU may be paired with a vision-specialized device for better performance on pixel-level processing.
Graphics Processing Units
High-performance GPUs deliver massive amounts of parallel computing potential, and graphics processors can be used to accelerate the portions of the computer vision pipeline that perform parallel processing on pixel data. While General Purpose GPUs (GPGPUs) have primarily been used for high-performance computing (HPC), even mobile graphics processors and integrated graphics cores are gaining GPGPU capability—meeting the power constraints for a wider range of vision applications. In designs that require 3D processing in addition to embedded vision, a GPU will already be part of the system and can be used to assist a general-purpose CPU with many computer vision algorithms. Many examples exist of x86-based embedded systems with discrete GPGPUs.
Digital Signal Processors
DSPs are very efficient for processing streaming data, since the bus and memory architecture are optimized to process high-speed data as it traverses the system. This architecture makes DSPs an excellent solution for processing image pixel data as it streams from a sensor source. Many DSPs for vision have been enhanced with coprocessors that are optimized for processing video inputs and accelerating computer vision algorithms. The specialized nature of DSPs makes these devices inefficient for processing general-purpose software workloads, so DSPs are usually paired with a RISC processor to create a heterogeneous computing environment that offers the best of both worlds.
Field Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs)
Instead of incurring the high cost and long lead-times for a custom ASIC to accelerate computer vision systems, designers can implement an FPGA to offer a reprogrammable solution for hardware acceleration. With millions of programmable gates, hundreds of I/O pins, and compute performance in the trillions of multiply-accumulates/sec (tera-MACs), high-end FPGAs offer the potential for highest performance in a vision system. Unlike a CPU, which has to time-slice or multi-thread tasks as they compete for compute resources, an FPGA has the advantage of being able to simultaneously accelerate multiple portions of a computer vision pipeline. Since the parallel nature of FPGAs offers so much advantage for accelerating computer vision, many of the algorithms are available as optimized libraries from semiconductor vendors. These computer vision libraries also include preconfigured interface blocks for connecting to other vision devices, such as IP cameras.
Vision-Specific Processors and Cores
Application-specific standard products (ASSPs) are specialized, highly integrated chips tailored for specific applications or application sets. ASSPs may incorporate a CPU, or use a separate CPU chip. By virtue of their specialization, ASSPs for vision processing typically deliver superior cost- and energy-efficiency compared with other types of processing solutions. Among other techniques, ASSPs deliver this efficiency through the use of specialized coprocessors and accelerators. And, because ASSPs are by definition focused on a specific application, they are usually provided with extensive associated software. This same specialization, however, means that an ASSP designed for vision is typically not suitable for other applications. ASSPs’ unique architectures can also make programming them more difficult than with other kinds of processors; some ASSPs are not user-programmable.

Quadric’s SDK Selected by TIER IV for AI Processing Evaluation and Optimization, Supporting Autoware Deployment in Next-Generation Autonomous Vehicles
Quadric today announced that TIER IV, Inc., of Japan has signed a license to use the Chimera AI processor SDK to evaluate and optimize future iterations of Autoware, open-source software for autonomous driving pioneered by TIER IV. Burlingame, CA, January 14, 2026 – Quadric today announced that TIER IV, Inc., of Japan has signed a

Deep Learning Vision Systems for Industrial Image Processing
This blog post was originally published at Basler’s website. It is reprinted here with the permission of Basler. Deep learning vision systems are often already a central component of industrial image processing. They enable precise error detection, intelligent quality control, and automated decisions – wherever conventional image processing methods reach their limits. We show how a

Upcoming Webinar on Advances in Automatic Test Pattern Generation
On January 14, 2026, at 7:00 am EST (10:00 am EST) Alliance Member company Synopsys will deliver a webinar “Advances in ATPG: From Power and Timing Awareness to Intelligent Pattern Search with AI” From the event page: As System-on-Chip (SoC) designs become increasingly complex, meeting test quality and cost goals requires advances in automatic test

Empowering Professionals and Aspiring Creators, Snapdragon X2 Plus Delivers Multi-day Battery Life, Fast Performance and Advanced AI
Key Takeaways: Snapdragon® X2 Plus transforms every click and every moment for modern professionals, aspiring creators and everyday users, delivering speed, multi-day battery life and built-in AI features. Representing a bold leap forward, the newest entrant in the Snapdragon X Series platform broadens access to the advanced performance and premium experiences consumers and businesses expect, expanding the growing Windows 11 Copilot+ PC community. Snapdragon X2 Plus harnesses the power of the 3rd Gen Qualcomm Oryon™ CPU and an 80 TOPS NPU, with select devices from
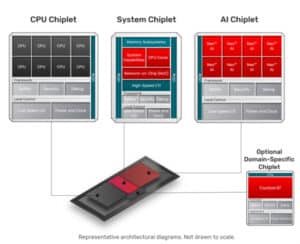
Cadence Launches Partner Ecosystem to Accelerate Chiplet Time to Market
Strategic collaborations with Samsung Foundry, Arm and others enable Cadence to deliver pre-validated chiplet solutions based on the Cadence Physical AI chiplet platform SAN JOSE, Calif., January 6, 2026, — Cadence (Nasdaq: CDNS) today announced a Chiplet Spec-to-Packaged Parts ecosystem to reduce engineering complexity and accelerate time to market for customers developing chiplets targeting physical

Intel Core Ultra Series 3 Debut as First Built on Intel 18A
Intel ushers in the next generation of AI PCs with exceptional performance, graphics and battery life; available this month Key Takeaways: First platform built on Intel 18A: At CES 2026, Intel launched the Intel® Core™ Ultra Series 3 processors, the first compute platform built on Intel 18A – the most advanced semiconductor process ever developed and
AMD Introduces Ryzen AI Embedded Processor Portfolio, Powering AI-Driven Immersive Experiences in Automotive, Industrial and Physical AI
Key Takeaways: New AMD Ryzen™ AI Embedded P100 and X100 Series processors combine high-performance “Zen 5” CPU cores, an AMD RDNA™ 3.5 GPU and an AMD XDNA™ 2 NPU for low-power AI acceleration Delivers energy-efficient, low-latency AI on a single chip for immersive in-vehicle experiences, industrial automation and physical AI for autonomous systems Launching today,

Qualcomm Drives the Future of Mobility with Strong Snapdragon Digital Chassis Momentum and Agentic AI for Major Global Automakers Worldwide
Key Takeaways: Qualcomm extends its automotive leadership with new collaborations, including Google, to power next‑gen software‑defined vehicles and agentic AI‑driven personalization. Snapdragon Ride and Cockpit Elite Platforms, and Snapdragon Ride Flex SoC, see rapid adoption, adding new design-wins and delivering the industry’s first commercialized mixed‑criticality platform that integrates cockpit, advanced driver‑assistance systems, and end‑to‑end AI. Decade of in-vehicle infotainment

SiMa.ai Announces First Integrated Capability with Synopsys to Accelerate Automotive Physical AI Development
San Jose, California – January 6, 2026 – SiMa.ai today announced the first integrated capability resulting from its strategic collaboration with Synopsys. The joint solution provides a blueprint to accelerate architecture exploration and early virtual software development for AI- ready, next-generation automotive SoCs that support applications such as Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) and In-vehicle-Infotainment

D3 Embedded Showcases Camera/Radar Fusion, ADAS Cameras, Driver Monitoring, and LWIR solutions at CES
Las Vegas, NV, January 7, 2026 — D3 Embedded is showcasing a suite of technology solutions in partnership with fellow Edge AI and Vision Alliance Members HTEC, STMicroelectronics and Texas Instruments at CES 2026. Solutions include driver and in-cabin monitoring, ADAS, surveillance, targeting and human tracking – and will be viewable at different locations within

Ambarella Launches Powerful Edge AI 8K Vision SoC With Industry-Leading AI and Multi-Sensor Perception Performance
New 4nm CV7 System-on-Chip Provides Ideal Combination of Simultaneous Multi-Stream Video and Advanced On-Device Edge AI Processing With Very Low Power Consumption SANTA CLARA, Calif., Jan. 05, 2026 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) — Ambarella, Inc. (NASDAQ: AMBA), an edge AI semiconductor company, today announced during CES the CV7 edge AI vision system-on-chip (SoC), which is optimized for a wide range

Qualcomm’s IE‑IoT Expansion Is Complete: Edge AI Unleashed for Developers, Enterprises & OEMs
Key Takeaways: Expanded set of processors, software, services, and developer tools including offerings and technologies from the five acquisitions of Augentix, Arduino, Edge Impulse, Focus.AI, and Foundries.io, positions the Company to help meet edge computing and AI needs for customers across virtually all verticals. Completed acquisition of Augentix, a leader in mass-market image processors, extends Qualcomm Technologies’ ability to provide system-on-chips tailored for intelligent IP cameras and vision systems. New Qualcomm Dragonwing™ Q‑7790 and Q‑8750 processors power security-focused on‑device AI across drones, smart cameras

NXP and GE HealthCare Accelerate AI Innovation in Acute Care
NXP and GE HealthCare announced a collaboration to pioneer new advancements in edge AI innovation, beginning with new anesthesia and neonatal concepts showcased at CES 2026. LAS VEGAS and CHICAGO, Illinois, January 6, 2026 — NXP Semiconductors N.V. (NASDAQ: NXPI) and GE HealthCare (NASDAQ: GEHC) today announced a collaboration to pioneer new advancements in
Accelerate AI Inference for Edge and Robotics with NVIDIA Jetson T4000 and NVIDIA JetPack 7.1
This blog post was originally published at NVIDIA’s website. It is reprinted here with the permission of NVIDIA. NVIDIA is introducing the NVIDIA Jetson T4000, bringing high-performance AI and real-time reasoning to a wider range of robotics and edge AI applications. Optimized for tighter power and thermal envelopes, T4000 delivers up to 1200 FP4 TFLOPs of AI compute and 64 GB of memory,

Qualcomm Introduces a Full Suite of Robotics Technologies, Powering Physical AI from Household Robots up to Full-Size Humanoids
Key Takeaways: Utilizing leadership in Physical AI with comprehensive stack systems built on safety-grade high performance SoC platforms, Qualcomm’s general-purpose robotics architecture delivers industry-leading power efficiency, and scalability, enabling capabilities from personal service robots to next generation industrial autonomous mobile robots and full-size humanoids that can reason, adapt, and decide. New end-to‑end architecture accelerates automation

TI Accelerates the Shift Toward Autonomous Vehicles with Expanded Automotive Portfolio
New analog and embedded processing technologies from TI enable automakers to deliver smarter, safer and more connected driving experiences across their entire vehicle fleet Key Takeaways: TI’s newest family of high-performance computing SoCs delivers safe, efficient edge AI performance up to 1200 TOPS with a proprietary NPU and chiplet-ready design. Automakers can simplify radar designs and

Synopsys Showcases Vision For AI-Driven, Software-Defined Automotive Engineering at CES 2026
Synopsys solutions accelerate innovation from systems to silicon, enabling more than 90% of the top 100 automotive suppliers to boost engineering productivity, predict system performance, and deliver safer, more sustainable mobility Key Takeaways: Synopsys will support the Fédération Internationale de l’Automobile (FIA), the global governing body for motorsport and the federation for mobility organizations

Cognitum Recognized as CES 2026 Honoree
Las Vegas, NV — CES — Cognitum, by ChipStart®, was recognized as a CES 2026 Honoree in embedded technologies, a distinction that reflects both the quality of the work and the impact of its design. The award highlights Cognitum’s innovative semiconductor architecture, which enables an ultra-low-power, high-performance AI processor built for the next generation of

NXP Advances Edge AI Leadership with New eIQ Agentic AI Framework
Key Takeaways: New eIQ Agentic AI Framework enables autonomous agentic intelligence at the edge, adding a new pillar to NXP’s edge AI platform Brings agentic AI to the edge, delivering real-time autonomous decision making for use cases requiring low latency, high reliability and data privacy Trusted foundation for both experienced and new developers to rapidly

Ambarella Launches a Developer Zone to Broaden its Edge AI Ecosystem
SANTA CLARA, Calif., Jan. 6, 2026 — Ambarella, Inc. (NASDAQ: AMBA), an edge AI semiconductor company, today announced during CES the launch of its Ambarella Developer Zone (DevZone). Located at developer.ambarella.com, the DevZone is designed to help Ambarella’s growing ecosystem of partners learn, build and deploy edge AI applications on a variety of edge systems with greater speed and clarity. It

