Processors for Embedded Vision
THIS TECHNOLOGY CATEGORY INCLUDES ANY DEVICE THAT EXECUTES VISION ALGORITHMS OR VISION SYSTEM CONTROL SOFTWARE
This technology category includes any device that executes vision algorithms or vision system control software. The following diagram shows a typical computer vision pipeline; processors are often optimized for the compute-intensive portions of the software workload.

The following examples represent distinctly different types of processor architectures for embedded vision, and each has advantages and trade-offs that depend on the workload. For this reason, many devices combine multiple processor types into a heterogeneous computing environment, often integrated into a single semiconductor component. In addition, a processor can be accelerated by dedicated hardware that improves performance on computer vision algorithms.
General-purpose CPUs
While computer vision algorithms can run on most general-purpose CPUs, desktop processors may not meet the design constraints of some systems. However, x86 processors and system boards can leverage the PC infrastructure for low-cost hardware and broadly-supported software development tools. Several Alliance Member companies also offer devices that integrate a RISC CPU core. A general-purpose CPU is best suited for heuristics, complex decision-making, network access, user interface, storage management, and overall control. A general purpose CPU may be paired with a vision-specialized device for better performance on pixel-level processing.
Graphics Processing Units
High-performance GPUs deliver massive amounts of parallel computing potential, and graphics processors can be used to accelerate the portions of the computer vision pipeline that perform parallel processing on pixel data. While General Purpose GPUs (GPGPUs) have primarily been used for high-performance computing (HPC), even mobile graphics processors and integrated graphics cores are gaining GPGPU capability—meeting the power constraints for a wider range of vision applications. In designs that require 3D processing in addition to embedded vision, a GPU will already be part of the system and can be used to assist a general-purpose CPU with many computer vision algorithms. Many examples exist of x86-based embedded systems with discrete GPGPUs.
Digital Signal Processors
DSPs are very efficient for processing streaming data, since the bus and memory architecture are optimized to process high-speed data as it traverses the system. This architecture makes DSPs an excellent solution for processing image pixel data as it streams from a sensor source. Many DSPs for vision have been enhanced with coprocessors that are optimized for processing video inputs and accelerating computer vision algorithms. The specialized nature of DSPs makes these devices inefficient for processing general-purpose software workloads, so DSPs are usually paired with a RISC processor to create a heterogeneous computing environment that offers the best of both worlds.
Field Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs)
Instead of incurring the high cost and long lead-times for a custom ASIC to accelerate computer vision systems, designers can implement an FPGA to offer a reprogrammable solution for hardware acceleration. With millions of programmable gates, hundreds of I/O pins, and compute performance in the trillions of multiply-accumulates/sec (tera-MACs), high-end FPGAs offer the potential for highest performance in a vision system. Unlike a CPU, which has to time-slice or multi-thread tasks as they compete for compute resources, an FPGA has the advantage of being able to simultaneously accelerate multiple portions of a computer vision pipeline. Since the parallel nature of FPGAs offers so much advantage for accelerating computer vision, many of the algorithms are available as optimized libraries from semiconductor vendors. These computer vision libraries also include preconfigured interface blocks for connecting to other vision devices, such as IP cameras.
Vision-Specific Processors and Cores
Application-specific standard products (ASSPs) are specialized, highly integrated chips tailored for specific applications or application sets. ASSPs may incorporate a CPU, or use a separate CPU chip. By virtue of their specialization, ASSPs for vision processing typically deliver superior cost- and energy-efficiency compared with other types of processing solutions. Among other techniques, ASSPs deliver this efficiency through the use of specialized coprocessors and accelerators. And, because ASSPs are by definition focused on a specific application, they are usually provided with extensive associated software. This same specialization, however, means that an ASSP designed for vision is typically not suitable for other applications. ASSPs’ unique architectures can also make programming them more difficult than with other kinds of processors; some ASSPs are not user-programmable.
NXP’s New S32N7 Unlocks the Full Potential of SDVs
Key Takeaways: S32N7 processor series fully digitizes and centralizes core vehicle functions OEMs can cut complexity and unlock AI-powered innovation fleetwide Bosch is the first to deploy the S32N7 in its vehicle integration platform LAS VEGAS, Jan. 05, 2026 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) — CES — NXP Semiconductors N.V. (NASDAQ: NXPI) today unveiled the S32N7 super-integration processor series, building

Chips&Media and Visionary.ai Unveil the World’s First AI-Based Full Image Signal Processor, Redefining the Future of Image Quality
The collaboration marks a breakthrough in real-time video, bringing software-upgradable imaging to the edge. 5th January, 2026 Seoul, South Korea and Jerusalem, Israel — Chips&Media, Inc. (KOSDAQ:094360) a leading hardware IP provider with more than 20 years of leadership in the multimedia industry, and Visionary.ai, the Israeli startup pioneering AI software for image processing,
Samsung to Launch In-house Mobile GPU by 2027
December 25, 2025, Suwon, South Korea — Samsung Electronics is accelerating plans to bring mobile graphics processing fully in-house, with multiple reports pointing to a proprietary GPU architecture arriving in an Exynos application processor as early as 2027. A report citing Cailian Press, says Samsung’s System LSI Division is pushing toward a “100% proprietary technology”

Groq and Nvidia Enter Non-Exclusive Inference Technology Licensing Agreement to Accelerate AI Inference at Global Scale
Mountain View, CA, December 24 — Today, Groq announced that it has entered into a non-exclusive licensing agreement with Nvidia for Groq’s inference technology. The agreement reflects a shared focus on expanding access to high-performance, low cost inference. As part of this agreement, Jonathan Ross, Groq’s Founder, Sunny Madra, Groq’s President, and other members of

Lattice Enhances sensAI Solution Stack with Edge AI Performance, Efficiency, and Ease of Use
Latest Lattice sensAI™ solution stack delivers industry-leading power efficiency, expanded AI model support, and flexible deployment tools for next-generation edge applications HILLSBORO, Ore. – Dec. 18, 2025 – Lattice Semiconductor (NASDAQ: LSCC), the low power programmable leader, today announced the latest release of the Lattice sensAI™ solution stack delivering expanded model support, enhanced AI performance, and greater deployment

How FPGA-Based Frame Grabbers Are Powering Next-Gen Multi-Camera Systems
This article was originally published at e-con Systems’ website. It is reprinted here with the permission of e-con Systems. FPGA-based frame grabbers are redefining multi-camera vision by enabling synchronized aggregation of up to eight GMSL streams for autonomous driving, robotics, and industrial automation. They overcome bandwidth and latency limits of USB and Ethernet by using PCIe

Arm at NeurIPS 2025: How AI Research is Shaping the Future of Intelligent Computing
This blog post was originally published at Arm’s website. It is reprinted here with the permission of Arm. NeurIPS 2025 provided Arm with a unique opportunity to share the latest technical trends and insights with the global AI research community. NeurIPS is one of the world’s leading AI research conferences, acting as a thriving global hub for

The Architecture Shift Powering Next-Gen Industrial AI
This blog post was originally published at Arm’s website. It is reprinted here with the permission of Arm. How Arm is powering the shift to flexible AI-ready, energy-efficient compute at the “Industrial Edge.” Industrial automation is undergoing a foundational shift. From industrial PC to edge gateways and smart sensors, compute needs at the edge are changing fast. AI is moving
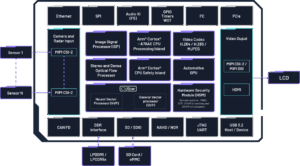
Ambarella’s CV3-AD655 Surround View with IMG BXM GPU: A Case Study
The CV3-AD family block diagram. This blog post was originally published at Imagination Technologies’ website. It is reprinted here with the permission of Imagination Technologies. Ambarella’s CV3-AD655 autonomous driving AI domain controller pairs energy-efficient compute with Imagination’s IMG BXM GPU to enable real-time surround-view visualisation for L2++/L3 vehicles. This case study outlines the industry shift

e-con Systems to Launch Darsi Pro, an NVIDIA Jetson-Powered AI Compute Box for Advanced Vision Applications
This blog post was originally published at e-con Systems’ website. It is reprinted here with the permission of e-con Systems. This blog offers expert insights into Darsi Pro, how it delivers a unified vision solution, and what it brings to alleviate modern workloads. Darsi Pro comes with GMSL camera options, rugged design, OTA support, and

Overcoming the Skies: Navigating the Challenges of Drone Autonomy
This blog post was originally published at Inuitive’s website. It is reprinted here with the permission of Inuitive. From early military prototypes to today’s complex commercial operations, drones have evolved from experimental aircraft into essential tools across industries. Since the FAA issued its first commercial permit in 2006, applications have rapidly expanded—from disaster relief and

AMD Spartan UltraScale+ FPGA Kit Adds Proven Infineon HyperRAM Support for Edge AI Designs
Somewhat eclipsed by last week’s announcement that the AMD Spartan™ UltraScale+™ FPGA SCU35 Evaluation Kit is now available, AMD and Infineon have disclosed successful validation of Infineon’s 64-Mb HYPERRAM™ memory and HYPERRAM controller IP on the platform. This collaboration expands the kit’s value for engineers building edge AI and computer vision systems. The SCU35 kit,

NVIDIA and Synopsys Announce Strategic Partnership to Revolutionize Engineering and Design
Key Highlights Multiyear collaboration spans NVIDIA CUDA accelerated computing, agentic and physical AI, and Omniverse digital twins to achieve simulation speed and scale previously unattainable through traditional CPU computing — opening new market opportunities across engineering. To further adoption of GPU-accelerated engineering solutions, the companies will collaborate in engineering and marketing activities. NVIDIA invested $2
Now Available: AMD Spartan UltraScale+ FPGA SCU35 Evaluation Kit–An Affordable Platform for Every Developer
November 25, 2025 The AMD Spartan™ UltraScale+™ FPGA SCU35 Evaluation Kit is now available for order. Built by AMD, this platform offers customers an accelerated path to production with Spartan UltraScale+ FPGAs. The kit features the Spartan UltraScale+ SU35P device that offers I/O expansion and board management capabilities. It also brings several new advances to

The 8-Series Reimagined: Snapdragon 8 Gen 5 Delivers Premium Performance and Experiences
San Diego, California November 25, 2025 — Qualcomm Technologies, Inc. today announced the Snapdragon® 8 Gen 5 Mobile Platform, a premium offering that combines outstanding performance with cutting-edge technologies, raising the bar for flagship mobile experiences. Key Takeaways: The Snapdragon 8-series continues to expand premium smartphone technologies, fueling many of the world’s leading flagship devices,

Microcontrollers Enter a New Growth Cycle as the Market Targets US$34 Billion in 2030
This market research report was originally published at the Yole Group’s website. It is reprinted here with the permission of the Yole Group. Yole Group releases its annual Status of the Microcontroller Industry report and expands its quarterly Microcontroller Market Monitor, delivering long-range strategic insights and detailed market tracking Key Takeaways: The global MCU market

Nota AI Signs Technology Collaboration Agreement with Samsung Electronics for Exynos AI Optimization “Driving the Popularization of On-Device Generative AI”
Nota AI’s optimization technology integrated into Samsung Electronics’ Exynos AI Studio, enhancing efficiency in on-device AI model development Seoul, South Korea Nov.26, 2025 — Nota AI, a company specializing in AI model compression and optimization, announced today that it has signed a collaboration agreement with Samsung Electronics’ System LSI Business to provide its AI

WAVE-N v2: Chips&Media’s Custom NPU Retains 16-bit FP for Superior Efficiency at High TOPS
Nov 26, 2025 Seoul, South Korea — Chips&Media is announcing that the next-generation customized NPU, WAVE-N v2, is ready for release, delivering higher computational power along with improved area and power efficiency. WAVE-N v2 is also designed to support a wider range of applications, such as object detection and segmentation, in addition to visual quality enhancement

Let’s Visit the Zoo
This blog post was originally published at Quadric’s website. It is reprinted here with the permission of Quadric. The term “model zoo” first gained prominence in the world of AI / machine learning beginning in the 2016-2017 timeframe. Originally used to describe open-source public repositories of working AI models – the most prominent of which today

Cadence Adds 10 New VIP to Strengthen Verification IP Portfolio for AI Designs
This article was originally published at Cadence’s website. It is reprinted here with the permission of Cadence. Cadence has unveiled 10 Verification IP (VIP) for key emerging interfaces tuned for AI-based designs, including Ultra Accelerator Link (UALink), Ultra Ethernet (UEC), LPDDR6, UCIe 3.0, AMBA CHI-H, Embedded USB v2 (eUSB2), and UniPro 3.0. These new VIP will

