Processors for Embedded Vision
THIS TECHNOLOGY CATEGORY INCLUDES ANY DEVICE THAT EXECUTES VISION ALGORITHMS OR VISION SYSTEM CONTROL SOFTWARE
This technology category includes any device that executes vision algorithms or vision system control software. The following diagram shows a typical computer vision pipeline; processors are often optimized for the compute-intensive portions of the software workload.

The following examples represent distinctly different types of processor architectures for embedded vision, and each has advantages and trade-offs that depend on the workload. For this reason, many devices combine multiple processor types into a heterogeneous computing environment, often integrated into a single semiconductor component. In addition, a processor can be accelerated by dedicated hardware that improves performance on computer vision algorithms.
General-purpose CPUs
While computer vision algorithms can run on most general-purpose CPUs, desktop processors may not meet the design constraints of some systems. However, x86 processors and system boards can leverage the PC infrastructure for low-cost hardware and broadly-supported software development tools. Several Alliance Member companies also offer devices that integrate a RISC CPU core. A general-purpose CPU is best suited for heuristics, complex decision-making, network access, user interface, storage management, and overall control. A general purpose CPU may be paired with a vision-specialized device for better performance on pixel-level processing.
Graphics Processing Units
High-performance GPUs deliver massive amounts of parallel computing potential, and graphics processors can be used to accelerate the portions of the computer vision pipeline that perform parallel processing on pixel data. While General Purpose GPUs (GPGPUs) have primarily been used for high-performance computing (HPC), even mobile graphics processors and integrated graphics cores are gaining GPGPU capability—meeting the power constraints for a wider range of vision applications. In designs that require 3D processing in addition to embedded vision, a GPU will already be part of the system and can be used to assist a general-purpose CPU with many computer vision algorithms. Many examples exist of x86-based embedded systems with discrete GPGPUs.
Digital Signal Processors
DSPs are very efficient for processing streaming data, since the bus and memory architecture are optimized to process high-speed data as it traverses the system. This architecture makes DSPs an excellent solution for processing image pixel data as it streams from a sensor source. Many DSPs for vision have been enhanced with coprocessors that are optimized for processing video inputs and accelerating computer vision algorithms. The specialized nature of DSPs makes these devices inefficient for processing general-purpose software workloads, so DSPs are usually paired with a RISC processor to create a heterogeneous computing environment that offers the best of both worlds.
Field Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs)
Instead of incurring the high cost and long lead-times for a custom ASIC to accelerate computer vision systems, designers can implement an FPGA to offer a reprogrammable solution for hardware acceleration. With millions of programmable gates, hundreds of I/O pins, and compute performance in the trillions of multiply-accumulates/sec (tera-MACs), high-end FPGAs offer the potential for highest performance in a vision system. Unlike a CPU, which has to time-slice or multi-thread tasks as they compete for compute resources, an FPGA has the advantage of being able to simultaneously accelerate multiple portions of a computer vision pipeline. Since the parallel nature of FPGAs offers so much advantage for accelerating computer vision, many of the algorithms are available as optimized libraries from semiconductor vendors. These computer vision libraries also include preconfigured interface blocks for connecting to other vision devices, such as IP cameras.
Vision-Specific Processors and Cores
Application-specific standard products (ASSPs) are specialized, highly integrated chips tailored for specific applications or application sets. ASSPs may incorporate a CPU, or use a separate CPU chip. By virtue of their specialization, ASSPs for vision processing typically deliver superior cost- and energy-efficiency compared with other types of processing solutions. Among other techniques, ASSPs deliver this efficiency through the use of specialized coprocessors and accelerators. And, because ASSPs are by definition focused on a specific application, they are usually provided with extensive associated software. This same specialization, however, means that an ASSP designed for vision is typically not suitable for other applications. ASSPs’ unique architectures can also make programming them more difficult than with other kinds of processors; some ASSPs are not user-programmable.

Qualcomm Unveils AI200 and AI250: Redefining Rack-scale Data Center Inference Performance for the AI Era
Highlights: Qualcomm AI200 and AI250 solutions deliver rack-scale performance and superior memory capacity for fast data center generative AI inference at industry-leading total cost of ownership (TCO). Qualcomm AI250 introduces an innovative memory architecture, offering a generational leap in effective memory bandwidth and efficiency for AI workloads. Both solutions feature a rich software stack and

Unleash Real-time LiDAR Intelligence with BrainChip Akida On-chip AI
This blog post was originally published at BrainChip’s website. It is reprinted here with the permission of BrainChip. Accelerating LiDAR Point Cloud with BrainChip’s Akida™ PointNet++ Model. LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) technology is the key enabler for advanced Spatial AI—the ability of a machine to understand and interact with the physical world in three

Introducing Synaptics Astra SL2610: The Edge Processor Engineers Have Been Waiting For
This blog post was originally published at Synaptics’ website. It is reprinted here with the permission of Synaptics. There’s a growing tension in the world of connected products. On one side, engineers find themselves having to push microcontrollers far beyond their limits, resorting to bolted-on accelerators, extra parts and delicate pipelines just to keep pace

Renesas Adds Two New MCU Groups to Blazing Fast RA8 Series with 1GHz Performance and Embedded MRAM
RA8M2 Devices Address General-Purpose Applications and RA8D2 Devices Target High-End Graphics and HMI; Both Offer Dual-Core Options for Even More Horsepower TOKYO, Japan, October 22, 2025 ― Renesas Electronics Corporation (TSE:6723), a premier supplier of advanced semiconductor solutions, today introduced the RA8M2 and RA8D2 microcontroller (MCU) groups. Based on a 1 GHz Arm® Cortex®-M85 processor

AI Drives the Wheel: How Computing Power is Reshaping the Automotive Industry
This market research report was originally published at the Yole Group’s website. It is reprinted here with the permission of the Yole Group. In its new report, Automotive Computing and AI 2025, Yole Group analyzes the technological and market forces redefining vehicle intelligence, safety, and connectivity. The automotive industry is accelerating into a new era

NanoEdge AI Studio v5, the First AutoML Tool with Synthetic Data Generation
This blog post was originally published at STMicroelectronics’ website. It is reprinted here with the permission of STMicroelectronics. NanoEdge AI Studio v5 is the first AutoML tool for STM32 microcontrollers capable of generating anomaly data out of typical logs, thanks to a new feature we call Synthetic Data Generation. Additionally, the latest version makes it

“Three Big Topics in Autonomous Driving and ADAS,” an Interview with Valeo
Frank Moesle, Software Department Manager at Valeo, talks with Independent Journalist Junko Yoshida for the “Three Big Topics in Autonomous Driving and ADAS” interview at the May 2025 Embedded Vision Summit. In this on-stage interview, Moesle and Yoshida focus on trends and challenges in automotive technology, autonomous driving and ADAS.… “Three Big Topics in Autonomous

Andes Showcases Expanding RISC-V Ecosystem and Next-generation “Cuzco” High-performance CPU at RISC-V Summit North America 2025
San Jose, CA October 17, 2025 –– Andes Technology, a Founding Premier Member of RISC-V International and a leading supplier of high-efficiency, high-performance RISC-V processor IPs, will highlight its expanding ecosystem and preview its next-generation out-of-order CPU—code-named “Cuzco”—at RISC-V Summit North America 2025, taking place October 22–23 in Santa Clara, California. Building on its success in

“Toward Hardware-agnostic ADAS Implementations for Software-defined Vehicles,” a Presentation from Valeo
Frank Moesle, Software Department Manager at Valeo, presents the “Toward Hardware-agnostic ADAS Implementations for Software-defined Vehicles” tutorial at the May 2025 Embedded Vision Summit. ADAS (advanced-driver assistance systems) software has historically been tightly bound to the underlying system-on-chip (SoC). This software, especially for visual perception, has been extensively optimized for… “Toward Hardware-agnostic ADAS Implementations for
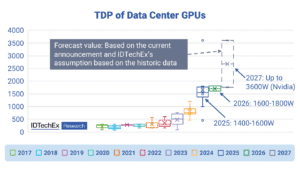
Two-Phase Liquid Cooling: The Future of High-end GPUs
As of 2025, single-phase direct-to-chip (D2C) liquid cooling remains the dominant solution for high-end GPU thermal management. However, with thermal design power (TDP) continuing to rise, the industry is approaching the limits of what single-phase cooling can handle. Two-phase D2C cooling is expected to enter large-scale deployment around 2027. IDTechEx has conducted extensive interviews across

Snapdragon Stories: Four Ways AI Has Improved My Life
This blog post was originally published at Qualcomm’s website. It is reprinted here with the permission of Qualcomm. I’ve used AI chat bots here and there, mostly for relatively simple and very specific tasks. But, I was underutilizing — and underestimating — how AI can quietly yet significantly reshape everyday moments. I don’t want to

Synaptics Launches the Next Generation of Astra Multimodal GenAI Processors to Power the Future of the Intelligent IoT Edge
San Jose, CA, October 15, 2025 – Synaptics® Incorporated (Nasdaq: SYNA) announces the new Astra™ SL2600 Series of multimodal Edge AI processors designed to deliver exceptional power and performance. The Astra SL2600 series enables a new generation of cost-effective intelligent devices that make the cognitive Internet of Things (IoT) possible. The SL2600 Series will launch

The Chiplet Calculus: Navigating the Integration Crisis at the Hardware.AD Frontier
A Tale of Two Cultures It is the best of times and the worst of times. The quest for fully autonomous vehicles (AVs) is increasingly a problem of hardware—but at a systems level, it’s a multi-faceted engineering challenge. The AD (Automated Driving) Europe 2025 conference in Berlin tackled this issue head-on this week. Far from

NVIDIA DGX Spark Arrives for World’s AI Developers
News Summary: NVIDIA founder and CEO Jensen Huang delivers DGX Spark to Elon Musk at SpaceX. This week, NVIDIA and its partners are shipping DGX Spark, the world’s smallest AI supercomputer, delivering NVIDIA’s AI stack in a compact desktop form factor. Acer, ASUS, Dell Technologies, GIGABYTE, HPI, Lenovo and MSI debut DGX Spark systems, expanding

Open-source Physics Engine and OpenUSD Advance Robot Learning
This blog post was originally published at NVIDIA’s website. It is reprinted here with the permission of NVIDIA. The Newton physics engine and enhanced NVIDIA Isaac GR00T models enable developers to accelerate robot learning through unified OpenUSD simulation workflows. Editor’s note: This blog is a part of Into the Omniverse, a series focused on how

Upcoming Workshop Explores Deploying PyTorch on the Edge
On October 21, 2022 at noon PT, Alliance Member company Qualcomm, along with Amazon, will deliver the free (advance registration required) half-day in-person workshop “PyTorch on the Edge: Amazon SageMaker x Qualcomm® AI Hub” at the InterContinental Hotel in San Francisco, California. From the event page: Seamless cloud-to-edge AI development experience: Train on AWS, deploy

D3 Embedded, HTEC, Texas Instruments and Tobii Pioneer the Integration of Single-camera and Radar Interior Sensor Fusion for In-cabin Sensing
The companies joined forces to develop sensor fusion based interior sensing for enhanced vehicle safety, launching at the InCabin Europe conference on October 7-9. Rochester, NY – October 6, 2025 – Tobii, with its automotive interior sensing branch Tobii Autosense, together with D3 Embedded, and HTEC today announced the development of an interior sensing solution

Chips&Media Completes RTL for ‘WAVE-P,’ the World’s First Standalone Advanced Professional Video (APV) Hardware CODEC IP
Chips&Media is now announcing that Advanced Professional Video CODEC development has been completed as committed to the ecosystem, and its final RTL is ready to be deployed to the market. The product name is WAVE-P, the world-first APV CODEC as an independent HW IP. Key notes: World-first, as an independent IP, APV HW CODEC for

Breaking Free from the CUDA Lock-in
This blog post was originally published at SiMa.ai’s website. It is reprinted here with the permission of SiMa.ai. The AI hardware landscape is dominated by one uncomfortable truth: most teams feel trapped by CUDA. You trained your models on NVIDIA GPUs, deployed them with TensorRT, and now the thought of switching hardware feels like rewriting

Upcoming Seminar Explores the Latest Innovations in Mobile Robotics
On October 22, 2022 at 9:00 am PT, Alliance Member company NXP Semiconductors, along with Avnet, will deliver a free (advance registration required) half-day in-person robotics seminar at NXP’s office in San Jose, California. From the event page: Join us for a free in-depth seminar exploring the latest innovations in mobile robotics with a focus

