Vision Algorithms for Embedded Vision
Most computer vision algorithms were developed on general-purpose computer systems with software written in a high-level language
Most computer vision algorithms were developed on general-purpose computer systems with software written in a high-level language. Some of the pixel-processing operations (ex: spatial filtering) have changed very little in the decades since they were first implemented on mainframes. With today’s broader embedded vision implementations, existing high-level algorithms may not fit within the system constraints, requiring new innovation to achieve the desired results.
Some of this innovation may involve replacing a general-purpose algorithm with a hardware-optimized equivalent. With such a broad range of processors for embedded vision, algorithm analysis will likely focus on ways to maximize pixel-level processing within system constraints.
This section refers to both general-purpose operations (ex: edge detection) and hardware-optimized versions (ex: parallel adaptive filtering in an FPGA). Many sources exist for general-purpose algorithms. The Embedded Vision Alliance is one of the best industry resources for learning about algorithms that map to specific hardware, since Alliance Members will share this information directly with the vision community.
General-purpose computer vision algorithms
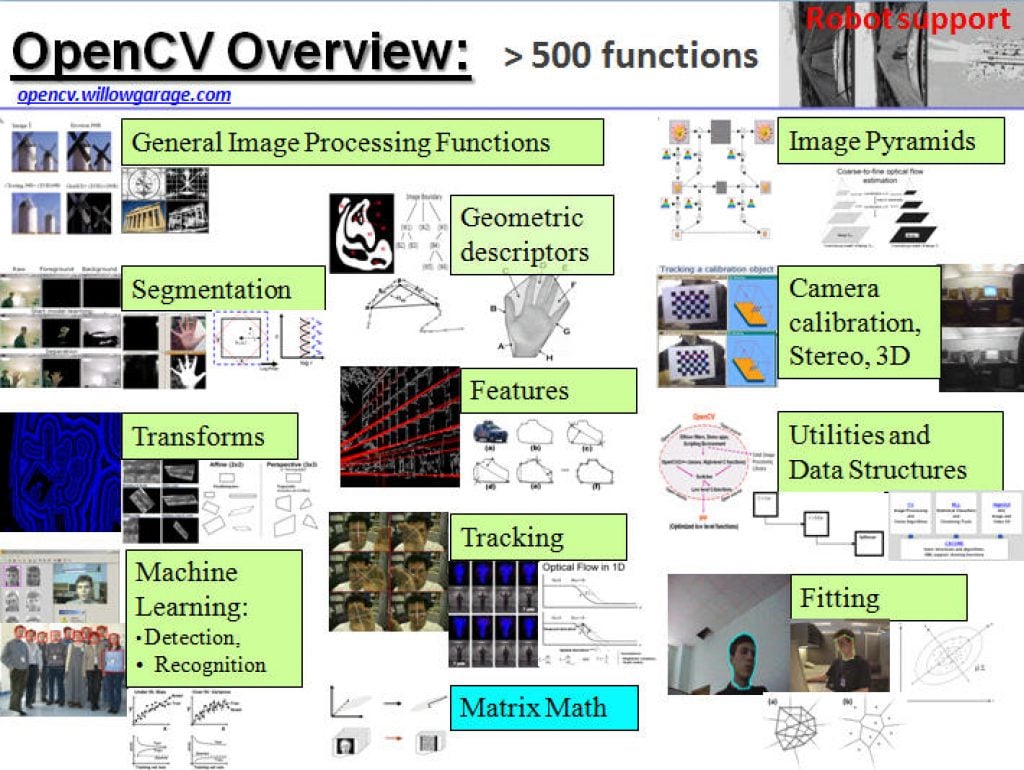
One of the most-popular sources of computer vision algorithms is the OpenCV Library. OpenCV is open-source and currently written in C, with a C++ version under development. For more information, see the Alliance’s interview with OpenCV Foundation President and CEO Gary Bradski, along with other OpenCV-related materials on the Alliance website.
Hardware-optimized computer vision algorithms
Several programmable device vendors have created optimized versions of off-the-shelf computer vision libraries. NVIDIA works closely with the OpenCV community, for example, and has created algorithms that are accelerated by GPGPUs. MathWorks provides MATLAB functions/objects and Simulink blocks for many computer vision algorithms within its Vision System Toolbox, while also allowing vendors to create their own libraries of functions that are optimized for a specific programmable architecture. National Instruments offers its LabView Vision module library. And Xilinx is another example of a vendor with an optimized computer vision library that it provides to customers as Plug and Play IP cores for creating hardware-accelerated vision algorithms in an FPGA.
Other vision libraries
- Halcon
- Matrox Imaging Library (MIL)
- Cognex VisionPro
- VXL
- CImg
- Filters

“Three Big Topics in Autonomous Driving and ADAS,” an Interview with Valeo
Frank Moesle, Software Department Manager at Valeo, talks with Independent Journalist Junko Yoshida for the “Three Big Topics in Autonomous Driving and ADAS” interview at the May 2025 Embedded Vision Summit. In this on-stage interview, Moesle and Yoshida focus on trends and challenges in automotive technology, autonomous driving and ADAS.… “Three Big Topics in Autonomous
Task-specific AI vs Generic LLMs: Why Precision and Reliability Matter
This blog post was originally published at Rapidflare’s website. It is reprinted here with the permission of Rapidflare. Task-specific AI is redefining what’s possible in mission-critical industries. While generic large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT excel at broad conversations, they often struggle with accuracy, consistency, and domain-specific context. In sectors where precision and reliability are

“Toward Hardware-agnostic ADAS Implementations for Software-defined Vehicles,” a Presentation from Valeo
Frank Moesle, Software Department Manager at Valeo, presents the “Toward Hardware-agnostic ADAS Implementations for Software-defined Vehicles” tutorial at the May 2025 Embedded Vision Summit. ADAS (advanced-driver assistance systems) software has historically been tightly bound to the underlying system-on-chip (SoC). This software, especially for visual perception, has been extensively optimized for… “Toward Hardware-agnostic ADAS Implementations for

Plainsight Appoints Venky Renganathan as Chief Technology Officer
Enterprise Technology Leader Brings Experience Leading Transformational Change as Computer Vision AI Innovator Moves to Next Phase of Platform Innovation SEATTLE — October 14, 2025 — Plainsight, a leader in computer vision AI solutions, today announced the appointment of Venky Renganathan as its new Chief Technology Officer (CTO). Renganathan is an enterprise technology leader with

Plainsight Names Jonathan Simkins as President & CFO
Proven enterprise leader brings expertise in managing privately-held companies during hyper-growth in machine learning, infrastructure software and open source. SEATTLE — September 30, 2025 — Plainsight, the leader in operationalizing computer vision through its pioneering modern computer vision infrastructure, today announced Jonathan Simkins as its President and CFO. In this role, Simkins will help scale

Snapdragon Stories: Four Ways AI Has Improved My Life
This blog post was originally published at Qualcomm’s website. It is reprinted here with the permission of Qualcomm. I’ve used AI chat bots here and there, mostly for relatively simple and very specific tasks. But, I was underutilizing — and underestimating — how AI can quietly yet significantly reshape everyday moments. I don’t want to

“Object Detection Models: Balancing Speed, Accuracy and Efficiency,” a Presentation from Union.ai
Sage Elliott, AI Engineer at Union.ai, presents the “Object Detection Models: Balancing Speed, Accuracy and Efficiency,” tutorial at the May 2025 Embedded Vision Summit. Deep learning has transformed many aspects of computer vision, including object detection, enabling accurate and efficient identification of objects in images and videos. However, choosing the… “Object Detection Models: Balancing Speed,

“Depth Estimation from Monocular Images Using Geometric Foundation Models,” a Presentation from Toyota Research Institute
Rareș Ambruș, Senior Manager for Large Behavior Models at Toyota Research Institute, presents the “Depth Estimation from Monocular Images Using Geometric Foundation Models” tutorial at the May 2025 Embedded Vision Summit. In this presentation, Ambruș looks at recent advances in depth estimation from images. He first focuses on the ability… “Depth Estimation from Monocular Images

Open-source Physics Engine and OpenUSD Advance Robot Learning
This blog post was originally published at NVIDIA’s website. It is reprinted here with the permission of NVIDIA. The Newton physics engine and enhanced NVIDIA Isaac GR00T models enable developers to accelerate robot learning through unified OpenUSD simulation workflows. Editor’s note: This blog is a part of Into the Omniverse, a series focused on how

“Introduction to DNN Training: Fundamentals, Process and Best Practices,” a Presentation from Think Circuits
Kevin Weekly, CEO of Think Circuits, presents the “Introduction to DNN Training: Fundamentals, Process and Best Practices” tutorial at the May 2025 Embedded Vision Summit. Training a model is a crucial step in machine learning, but it can be overwhelming for beginners. In this talk, Weekly provides a comprehensive introduction… “Introduction to DNN Training: Fundamentals,

Upcoming Workshop Explores Deploying PyTorch on the Edge
On October 21, 2022 at noon PT, Alliance Member company Qualcomm, along with Amazon, will deliver the free (advance registration required) half-day in-person workshop “PyTorch on the Edge: Amazon SageMaker x Qualcomm® AI Hub” at the InterContinental Hotel in San Francisco, California. From the event page: Seamless cloud-to-edge AI development experience: Train on AWS, deploy

D3 Embedded, HTEC, Texas Instruments and Tobii Pioneer the Integration of Single-camera and Radar Interior Sensor Fusion for In-cabin Sensing
The companies joined forces to develop sensor fusion based interior sensing for enhanced vehicle safety, launching at the InCabin Europe conference on October 7-9. Rochester, NY – October 6, 2025 – Tobii, with its automotive interior sensing branch Tobii Autosense, together with D3 Embedded, and HTEC today announced the development of an interior sensing solution

Breaking Free from the CUDA Lock-in
This blog post was originally published at SiMa.ai’s website. It is reprinted here with the permission of SiMa.ai. The AI hardware landscape is dominated by one uncomfortable truth: most teams feel trapped by CUDA. You trained your models on NVIDIA GPUs, deployed them with TensorRT, and now the thought of switching hardware feels like rewriting

Upcoming Seminar Explores the Latest Innovations in Mobile Robotics
On October 22, 2022 at 9:00 am PT, Alliance Member company NXP Semiconductors, along with Avnet, will deliver a free (advance registration required) half-day in-person robotics seminar at NXP’s office in San Jose, California. From the event page: Join us for a free in-depth seminar exploring the latest innovations in mobile robotics with a focus

Free Webinar Explores Edge AI-enabled Microcontroller Capabilities and Trends
On November 18, 2025 at 9 am PT (noon ET), the Yole Group’s Tom Hackenberg, principal analyst for computing, will present the free hour webinar “How AI-enabled Microcontrollers Are Expanding Edge AI Opportunities,” organized by the Edge AI and Vision Alliance. Here’s the description, from the event registration page: Running AI inference at the edge,

“Lessons Learned Building and Deploying a Weed-killing Robot,” a Presentation from Tensorfield Agriculture
Xiong Chang, CEO and Co-founder of Tensorfield Agriculture, presents the “Lessons Learned Building and Deploying a Weed-Killing Robot” tutorial at the May 2025 Embedded Vision Summit. Agriculture today faces chronic labor shortages and growing challenges around herbicide resistance, as well as consumer backlash to chemical inputs. Smarter, more sustainable approaches… “Lessons Learned Building and Deploying

