Vision Algorithms for Embedded Vision
Most computer vision algorithms were developed on general-purpose computer systems with software written in a high-level language
Most computer vision algorithms were developed on general-purpose computer systems with software written in a high-level language. Some of the pixel-processing operations (ex: spatial filtering) have changed very little in the decades since they were first implemented on mainframes. With today’s broader embedded vision implementations, existing high-level algorithms may not fit within the system constraints, requiring new innovation to achieve the desired results.
Some of this innovation may involve replacing a general-purpose algorithm with a hardware-optimized equivalent. With such a broad range of processors for embedded vision, algorithm analysis will likely focus on ways to maximize pixel-level processing within system constraints.
This section refers to both general-purpose operations (ex: edge detection) and hardware-optimized versions (ex: parallel adaptive filtering in an FPGA). Many sources exist for general-purpose algorithms. The Embedded Vision Alliance is one of the best industry resources for learning about algorithms that map to specific hardware, since Alliance Members will share this information directly with the vision community.
General-purpose computer vision algorithms
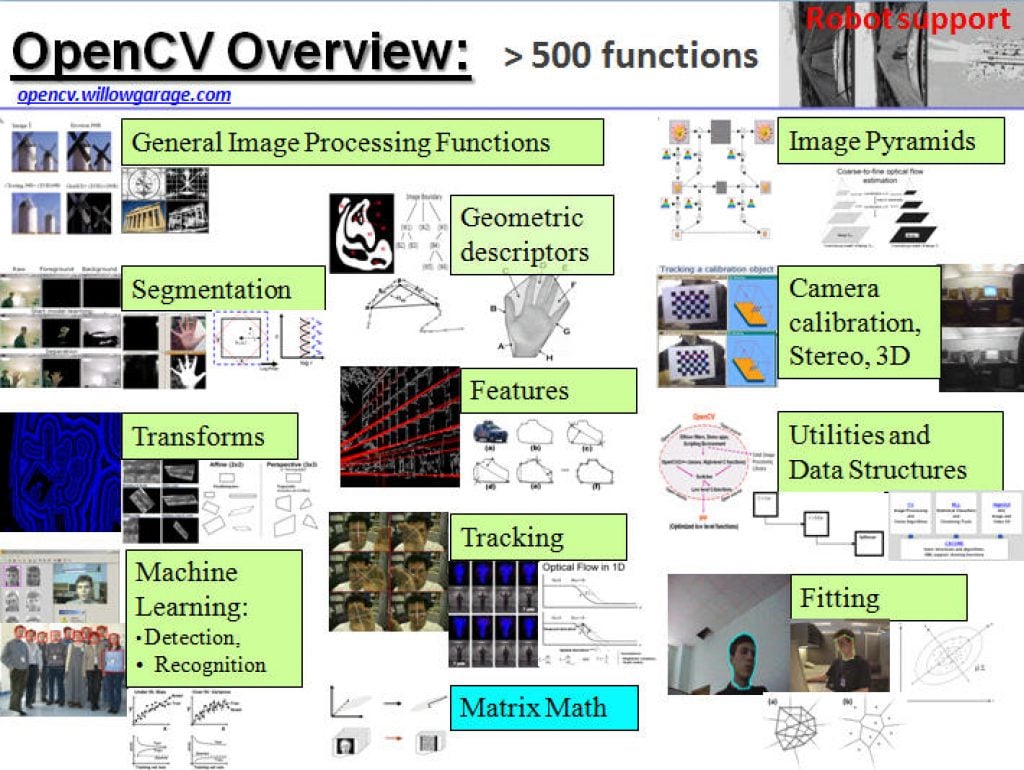
One of the most-popular sources of computer vision algorithms is the OpenCV Library. OpenCV is open-source and currently written in C, with a C++ version under development. For more information, see the Alliance’s interview with OpenCV Foundation President and CEO Gary Bradski, along with other OpenCV-related materials on the Alliance website.
Hardware-optimized computer vision algorithms
Several programmable device vendors have created optimized versions of off-the-shelf computer vision libraries. NVIDIA works closely with the OpenCV community, for example, and has created algorithms that are accelerated by GPGPUs. MathWorks provides MATLAB functions/objects and Simulink blocks for many computer vision algorithms within its Vision System Toolbox, while also allowing vendors to create their own libraries of functions that are optimized for a specific programmable architecture. National Instruments offers its LabView Vision module library. And Xilinx is another example of a vendor with an optimized computer vision library that it provides to customers as Plug and Play IP cores for creating hardware-accelerated vision algorithms in an FPGA.
Other vision libraries
- Halcon
- Matrox Imaging Library (MIL)
- Cognex VisionPro
- VXL
- CImg
- Filters
A Practical Guide to Recall, Precision, and NDCG
This blog post was originally published at Rapidflare’s website. It is reprinted here with the permission of Rapidflare. Introduction Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is revolutionizing how Large Language Models (LLMs) access and use information. By grounding models in domain specific data from authoritative sources, RAG systems deliver more accurate and context-aware answers. But a RAG system is

Google Adds “Agentic Vision” to Gemini 3 Flash
Jan. 30, 2026 — Google has announced Agentic Vision, a new capability in Gemini 3 Flash that turns image understanding into an active, tool-using workflow rather than a single “static glance.” Agentic Vision pairs visual reasoning with code execution (Python) so the model can iteratively zoom in, crop, annotate, and otherwise manipulate an image to

Robotics Builders Forum offers Hardware, Know-How and Networking to Developers
On February 25, 2026 from 8:30 am to 5:30 pm ET, Advantech, Qualcomm, Arrow, in partnership with D3 Embedded, Edge Impulse, and the Pittsburgh Robotics Network will present Robotics Builders Forum, an in-person conference for engineers and product teams. Qualcomm and D3 Embedded are members of the Edge AI and Vision Alliance, while Edge Impulse

On-Device LLMs in 2026: What Changed, What Matters, What’s Next
In On-Device LLMs: State of the Union, 2026, Vikas Chandra and Raghuraman Krishnamoorthi explain why running LLMs on phones has moved from novelty to practical engineering, and why the biggest breakthroughs came not from faster chips but from rethinking how models are built, trained, compressed, and deployed. Why run LLMs locally? Four reasons: latency (cloud
Getting Started with Edge AI on NVIDIA Jetson: LLMs, VLMs, and Foundation Models for Robotics
This article was originally published at NVIDIA’s website. It is reprinted here with the permission of NVIDIA. Running advanced AI and computer vision workloads on small, power-efficient devices at the edge is a growing challenge. Robots, smart cameras, and autonomous machines need real-time intelligence to see, understand, and react without depending on the cloud. The NVIDIA

Top Python Libraries of 2025
This article was originally published at Tryolabs’ website. It is reprinted here with the permission of Tryolabs. Welcome to the 11th edition of our yearly roundup of the Python libraries! If 2025 felt like the year of Large Language Models (LLMs) and agents, it’s because it truly was. The ecosystem expanded at incredible speed, with new models,

How to Enhance 3D Gaussian Reconstruction Quality for Simulation
This article was originally published at NVIDIA’s website. It is reprinted here with the permission of NVIDIA. Building truly photorealistic 3D environments for simulation is challenging. Even with advanced neural reconstruction methods such as 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) and 3D Gaussian with Unscented Transform (3DGUT), rendered views can still contain artifacts such as blurriness, holes, or

Deep Learning Vision Systems for Industrial Image Processing
This blog post was originally published at Basler’s website. It is reprinted here with the permission of Basler. Deep learning vision systems are often already a central component of industrial image processing. They enable precise error detection, intelligent quality control, and automated decisions – wherever conventional image processing methods reach their limits. We show how a

NVIDIA Unveils New Open Models, Data and Tools to Advance AI Across Every Industry
This post was originally published at NVIDIA’s website. It is reprinted here with the permission of NVIDIA. Expanding the open model universe, NVIDIA today released new open models, data and tools to advance AI across every industry. These models — spanning the NVIDIA Nemotron family for agentic AI, the NVIDIA Cosmos platform for physical AI, the new NVIDIA Alpamayo family for autonomous vehicle

ModelCat AI Partners with Alif Semiconductor to Deliver Rapid ML Model Onboarding to Customers
The partnership slashes model onboarding time to under 30 days, offering Alif customers a “Cursor-like” experience for building and deploying Edge AI models. SUNNYVALE, Calif., Jan. 6, 2026 (PRNewswire) — ModelCat AI, the creator of the world’s first fully autonomous AI model builder, today announced a strategic partnership with Alif Semiconductor, a global leader in

ChatTag: Bringing ChatGPT Vision to Image Annotation in OpenFilter
This blog post was originally published at Plainsight Technologies’ website. It is reprinted here with the permission of Plainsight Technologies. Image annotation has always been one of those tasks that’s both essential and tedious. Whether you’re labeling thousands of product photos for a retail model or identifying components in industrial footage, manual annotation is time-consuming and

Top 3 System Patterns Gemini 3 Pro Vision Unlocks for Edge Teams
For those who missed it in the holiday haze, Google’s Gemini 3 Pro launched on December 5th, but the push on vision isn’t just “better VQA.” Google frames it as a jump from recognition to visual + spatial reasoning, spanning documents, spatial, screens, and video. If you’re building edge AI products, that matters less as

Google Releases FunctionGemma: Lightweight Function-calling Model Aimed at On-device Agents
Google has released FunctionGemma, a specialized Gemma 3 270M model fine-tuned for function calling—turning natural-language commands into structured API/tool calls for local agents. Why this matters for edge AI engineers Local-first “action agents”: FunctionGemma is positioned as an on-device “action” model (or a lightweight controller that can route complex requests to larger models like Gemma

97% Smaller, Just as Smart: Scaling Down Networks with Structured Pruning
This article was originally published at Analog Devices’ website. It is reprinted here with the permission of Analog Devices. Why Smaller Models Matter Shrinking AI models isn’t just a nice-to-have—it’s a necessity for bringing powerful, real-time intelligence to edge devices. Whether it’s smartphones, wearables, or embedded systems, these platforms operate with strict memory, compute, and

AI On: 3 Ways to Bring Agentic AI to Computer Vision Applications
This blog post was originally published at NVIDIA’s website. It is reprinted here with the permission of NVIDIA. Learn how to integrate vision language models into video analytics applications, from AI-powered search to fully automated video analysis. Today’s computer vision systems excel at identifying what happens in physical spaces and processes, but lack the abilities to explain the

NVIDIA Debuts Nemotron 3 Family of Open Models
News Summary: The Nemotron 3 family of open models — in Nano, Super and Ultra sizes — introduces the most efficient family of open models with leading accuracy for building agentic AI applications. Nemotron 3 Nano delivers 4x higher throughput than Nemotron 2 Nano and delivers the most tokens per second for multi-agent systems at scale through a

