Vision Algorithms for Embedded Vision
Most computer vision algorithms were developed on general-purpose computer systems with software written in a high-level language
Most computer vision algorithms were developed on general-purpose computer systems with software written in a high-level language. Some of the pixel-processing operations (ex: spatial filtering) have changed very little in the decades since they were first implemented on mainframes. With today’s broader embedded vision implementations, existing high-level algorithms may not fit within the system constraints, requiring new innovation to achieve the desired results.
Some of this innovation may involve replacing a general-purpose algorithm with a hardware-optimized equivalent. With such a broad range of processors for embedded vision, algorithm analysis will likely focus on ways to maximize pixel-level processing within system constraints.
This section refers to both general-purpose operations (ex: edge detection) and hardware-optimized versions (ex: parallel adaptive filtering in an FPGA). Many sources exist for general-purpose algorithms. The Embedded Vision Alliance is one of the best industry resources for learning about algorithms that map to specific hardware, since Alliance Members will share this information directly with the vision community.
General-purpose computer vision algorithms
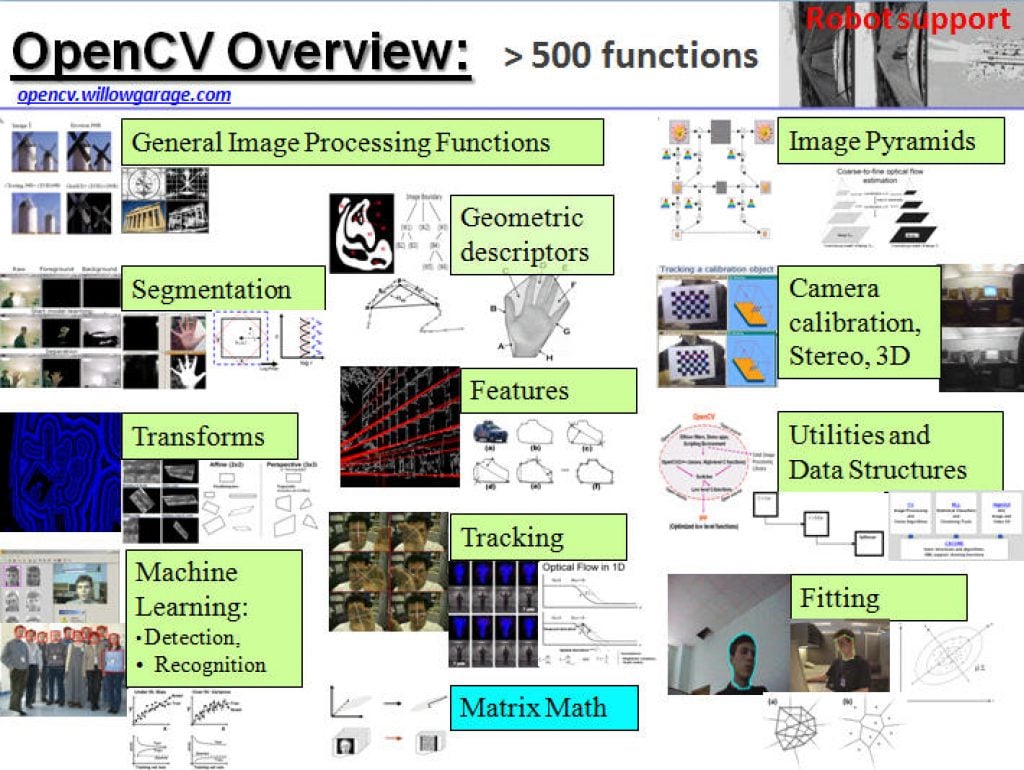
One of the most-popular sources of computer vision algorithms is the OpenCV Library. OpenCV is open-source and currently written in C, with a C++ version under development. For more information, see the Alliance’s interview with OpenCV Foundation President and CEO Gary Bradski, along with other OpenCV-related materials on the Alliance website.
Hardware-optimized computer vision algorithms
Several programmable device vendors have created optimized versions of off-the-shelf computer vision libraries. NVIDIA works closely with the OpenCV community, for example, and has created algorithms that are accelerated by GPGPUs. MathWorks provides MATLAB functions/objects and Simulink blocks for many computer vision algorithms within its Vision System Toolbox, while also allowing vendors to create their own libraries of functions that are optimized for a specific programmable architecture. National Instruments offers its LabView Vision module library. And Xilinx is another example of a vendor with an optimized computer vision library that it provides to customers as Plug and Play IP cores for creating hardware-accelerated vision algorithms in an FPGA.
Other vision libraries
- Halcon
- Matrox Imaging Library (MIL)
- Cognex VisionPro
- VXL
- CImg
- Filters

Using the Qualcomm AI Inference Suite from Google Colab
This blog post was originally published at Qualcomm’s website. It is reprinted here with the permission of Qualcomm. Building off of the blog post here, which shows how easy it is to call the Cirrascale AI Inference Cloud using the Qualcomm AI Inference Suite, we’ll use Google Colab to show the same scenario. In the previous blog

“Transformer Networks: How They Work and Why They Matter,” a Presentation from Synthpop AI
Rakshit Agrawal, Principal AI Scientist at Synthpop AI, presents the “Transformer Networks: How They Work and Why They Matter” tutorial at the May 2025 Embedded Vision Summit. Transformer neural networks have revolutionized artificial intelligence by introducing an architecture built around self-attention mechanisms. This has enabled unprecedented advances in understanding sequential… “Transformer Networks: How They Work

Deploy High-performance AI Models in Windows Applications on NVIDIA RTX AI PCs
This blog post was originally published at NVIDIA’s website. It is reprinted here with the permission of NVIDIA. Microsoft is now making Windows ML available to developers. Windows ML enables C#, C++ and Python developers to optimally run AI models locally across PC hardware from CPU, NPU and GPUs. On NVIDIA RTX GPUs, it utilizes

“Understanding Human Activity from Visual Data,” a Presentation from Sportlogiq
Mehrsan Javan, Chief Technology Officer at Sportlogiq, presents the “Understanding Human Activity from Visual Data” tutorial at the May 2025 Embedded Vision Summit. Activity detection and recognition are crucial tasks in various industries, including surveillance and sports analytics. In this talk, Javan provides an in-depth exploration of human activity understanding,… “Understanding Human Activity from Visual

“Multimodal Enterprise-scale Applications in the Generative AI Era,” a Presentation from Skyworks Solutions
Mumtaz Vauhkonen, Senior Director of AI at Skyworks Solutions, presents the “Multimodal Enterprise-scale Applications in the Generative AI Era” tutorial at the May 2025 Embedded Vision Summit. As artificial intelligence is making rapid strides in use of large language models, the need for multimodality arises in multiple application scenarios. Similar… “Multimodal Enterprise-scale Applications in the
How CLIKA’s Automated Hardware-aware AI Compression Toolkit Efficiently Enables Scalable Deployment of AI on Any Target Hardware
This blog post was originally published at CLIKA’s website. It is reprinted here with the permission of CLIKA. Organisations are making a shift from experimental spending on AI to long-term investments in this new technology but there are challenges involved. Here’s how CLIKA can help. With democratising AI and greater access to open-source AI models,

Using the Qualcomm AI Inference Suite Directly from a Web Page
This blog post was originally published at Qualcomm’s website. It is reprinted here with the permission of Qualcomm. Applying the Qualcomm AI Inference Suite directly from a web page using JavaScript makes it easy to create and understand how AI inference works in in web solutions. Qualcomm Technologies in collaboration with Cirrascale has a free-to-try

“Developing a GStreamer-based Custom Camera System for Long-range Biometric Data Collection,” a Presentation from Oak Ridge National Laboratory
Gavin Jager, Researcher and Lab Space Manager at Oak Ridge National Laboratory, presents the “Developing a GStreamer-based Custom Camera System for Long-range Biometric Data Collection” tutorial at the May 2025 Embedded Vision Summit. In this presentation, Jager describes Oak Ridge National Laboratory’s work developing software for a custom camera system… “Developing a GStreamer-based Custom Camera

“Sensors and Compute Needs and Challenges for Humanoid Robots,” a Presentation from Agility Robotics
Vlad Branzoi, Perception Sensors Team Lead at Agility Robotics, presents the “Sensors and Compute Needs and Challenges for Humanoid Robots” tutorial at the September 2025 Edge AI and Vision Innovation Forum.

How to Integrate Computer Vision Pipelines with Generative AI and Reasoning
This blog post was originally published at NVIDIA’s website. It is reprinted here with the permission of NVIDIA. Generative AI is opening new possibilities for analyzing existing video streams. Video analytics are evolving from counting objects to turning raw video content footage into real-time understanding. This enables more actionable insights. The NVIDIA AI Blueprint for

“Scaling Artificial Intelligence and Computer Vision for Conservation,” a Presentation from The Nature Conservancy
Matt Merrifield, Chief Technology Officer at The Nature Conservancy, presents the “Scaling Artificial Intelligence and Computer Vision for Conservation” tutorial at the May 2025 Embedded Vision Summit. In this presentation, Merrifield explains how the world’s largest environmental nonprofit is spearheading projects to scale the use of edge AI and vision… “Scaling Artificial Intelligence and Computer

“A Lightweight Camera Stack for Edge AI,” a Presentation from Meta
Jui Garagate, Camera Software Engineer, and Karthick Kumaran, Staff Software Engineer, both of Meta, co-present the “Lightweight Camera Stack for Edge AI” tutorial at the May 2025 Embedded Vision Summit. Electronic products for virtual and augmented reality, home robots and cars deploy multiple cameras for computer vision and AI use… “A Lightweight Camera Stack for

“Unlocking Visual Intelligence: Advanced Prompt Engineering for Vision-language Models,” a Presentation from LinkedIn Learning
Alina Li Zhang, Senior Data Scientist and Tech Writer at LinkedIn Learning, presents the “Unlocking Visual Intelligence: Advanced Prompt Engineering for Vision-language Models” tutorial at the May 2025 Embedded Vision Summit. Imagine a world where AI systems automatically detect thefts in grocery stores, ensure construction site safety and identify patient… “Unlocking Visual Intelligence: Advanced Prompt

The Edge’s Essential Role in the Future of AI
This blog post was originally published at Qualcomm’s website. It is reprinted here with the permission of Qualcomm. What you should know: The future of AI will be hybrid, with the cloud and the edge working together — each playing a vital role. The user interface (UI) is now human-centric — your device understands your

“Deploying Accelerated ML and AI: The Role of Khronos Open Standards,” a Presentation from the Khronos Group
Neil Trevett, President of the Khronos Group and Vice President of Developer Ecosystems at NVIDIA, presents the “Deploying Accelerated ML and AI: The Role of Khronos Open Standards” tutorial at the May 2025 Embedded Vision Summit. Accelerating machine learning and AI workloads often requires specialized hardware, but managing compatibility across… “Deploying Accelerated ML and AI:

“Scaling Computer Vision at the Edge,” a Presentation from Invisible AI
Eric Danziger, CEO of Invisible AI, presents the “Scaling Computer Vision at the Edge” tutorial at the May 2025 Embedded Vision Summit. In this presentation, Danziger introduces a comprehensive framework for scaling computer vision systems across three critical dimensions: capability evolution, infrastructure decisions and deployment scaling. Today’s leading-edge vision systems… “Scaling Computer Vision at the

