Vision Algorithms for Embedded Vision
Most computer vision algorithms were developed on general-purpose computer systems with software written in a high-level language
Most computer vision algorithms were developed on general-purpose computer systems with software written in a high-level language. Some of the pixel-processing operations (ex: spatial filtering) have changed very little in the decades since they were first implemented on mainframes. With today’s broader embedded vision implementations, existing high-level algorithms may not fit within the system constraints, requiring new innovation to achieve the desired results.
Some of this innovation may involve replacing a general-purpose algorithm with a hardware-optimized equivalent. With such a broad range of processors for embedded vision, algorithm analysis will likely focus on ways to maximize pixel-level processing within system constraints.
This section refers to both general-purpose operations (ex: edge detection) and hardware-optimized versions (ex: parallel adaptive filtering in an FPGA). Many sources exist for general-purpose algorithms. The Embedded Vision Alliance is one of the best industry resources for learning about algorithms that map to specific hardware, since Alliance Members will share this information directly with the vision community.
General-purpose computer vision algorithms
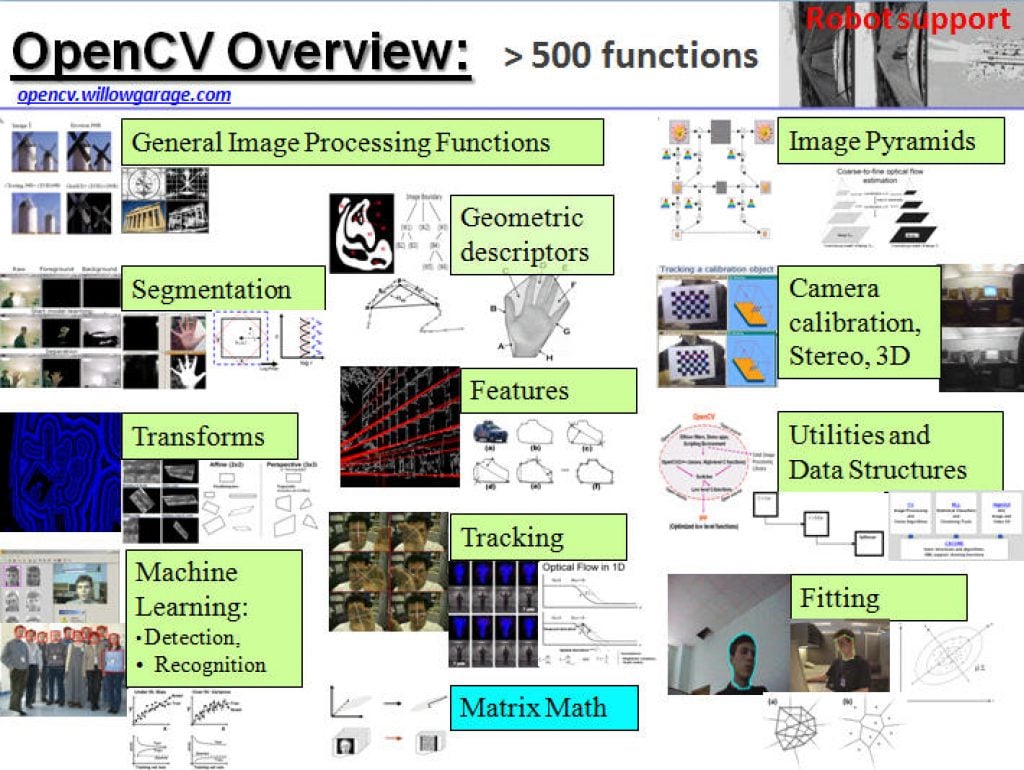
One of the most-popular sources of computer vision algorithms is the OpenCV Library. OpenCV is open-source and currently written in C, with a C++ version under development. For more information, see the Alliance’s interview with OpenCV Foundation President and CEO Gary Bradski, along with other OpenCV-related materials on the Alliance website.
Hardware-optimized computer vision algorithms
Several programmable device vendors have created optimized versions of off-the-shelf computer vision libraries. NVIDIA works closely with the OpenCV community, for example, and has created algorithms that are accelerated by GPGPUs. MathWorks provides MATLAB functions/objects and Simulink blocks for many computer vision algorithms within its Vision System Toolbox, while also allowing vendors to create their own libraries of functions that are optimized for a specific programmable architecture. National Instruments offers its LabView Vision module library. And Xilinx is another example of a vendor with an optimized computer vision library that it provides to customers as Plug and Play IP cores for creating hardware-accelerated vision algorithms in an FPGA.
Other vision libraries
- Halcon
- Matrox Imaging Library (MIL)
- Cognex VisionPro
- VXL
- CImg
- Filters

How Do You Teach an AI Model to Reason? With Humans
This blog post was originally published at NVIDIA’s website. It is reprinted here with the permission of NVIDIA. NVIDIA’s data factory team creates the foundation for AI models like Cosmos Reason, which today topped the physical reasoning leaderboard on Hugging Face. AI models are advancing at a rapid rate and scale. But what might they

“Scaling Machine Learning with Containers: Lessons Learned,” a Presentation from Instrumental
Rustem Feyzkhanov, Machine Learning Engineer at Instrumental, presents the “Scaling Machine Learning with Containers: Lessons Learned” tutorial at the May 2025 Embedded Vision Summit. In the dynamic world of machine learning, efficiently scaling solutions from research to production is crucial. In this presentation, Feyzkhanov explores the nuances of scaling machine… “Scaling Machine Learning with Containers:

PerCV.ai: How a Vision AI Platform and the STM32N6 can Turn Around an 80% Failure Rate for AI Projects
This blog post was originally published at STMicroelectronics’ website. It is reprinted here with the permission of STMicroelectronics. The vision AI platform PerCV.ai (pronounced Perceive AI), could be the secret weapon that enables a company to deploy an AI application when so many others fail. The solution from Irida Labs, a member of the ST

“Vision-language Models on the Edge,” a Presentation from Hugging Face
Cyril Zakka, Health Lead at Hugging Face, presents the “Vision-language Models on the Edge” tutorial at the May 2025 Embedded Vision Summit. In this presentation, Zakka provides an overview of vision-language models (VLMs) and their deployment on edge devices using Hugging Face’s recently released SmolVLM as an example. He examines… “Vision-language Models on the Edge,”

OwLite Meets Qualcomm Neural Network: Unlocking On-device AI Performance
This blog post was originally published at SqueezeBits’ website. It is reprinted here with the permission of SqueezeBits. At SqueezeBits we have been empowering developers to efficiently deploy complex AI models while minimizing performance trade-offs with OwLite toolkit. With OwLite v2.5, we’re excited to announce official support for Qualcomm Neural Network (QNN) through seamless integration

“Vision LLMs in Multi-agent Collaborative Systems: Architecture and Integration,” a Presentation from Google
Niyati Prajapati, ML and Generative AI Lead at Google, presents the “Vision LLMs in Multi-agent Collaborative Systems: Architecture and Integration” tutorial at the May 2025 Embedded Vision Summit. In this talk, Prajapati explores how vision LLMs can be used in multi-agent collaborative systems to enable new levels of capability and… “Vision LLMs in Multi-agent Collaborative
Shifting AI Inference from the Cloud to Your Phone Can Reduce AI Costs
This blog post was originally published at Qualcomm’s website. It is reprinted here with the permission of Qualcomm. Every AI query has a cost, and not just in dollars. Study shows distributing AI workloads to your devices — such as your smartphone — can reduce costs and decrease water consumption What you should know: Study

“Building Agentic Applications for the Edge,” a Presentation from GMAC Intelligence
Amit Mate, Founder and CEO of GMAC Intelligence, presents the “Building Agentic Applications for the Edge” tutorial at the May 2025 Embedded Vision Summit. Along with AI agents, the new generation of large language models, vision-language models and other large multimodal models are enabling powerful new capabilities that promise to… “Building Agentic Applications for the

How to Use the RGB-D Mapping Feature of e-con Systems’ DepthVista ToF Camera
This blog post was originally published at e-con Systems’ website. It is reprinted here with the permission of e-con Systems. Learn how to leverage the RGB-D mapping feature of e-con Systems’ DepthVista ToF camera to align RGB and depth data for precise 3D vision applications. This step-by-step guide covers camera calibration, the role of intrinsic

“Enabling Ego Vision Applications on Smart Eyewear Devices,” a Presentation from EssilorLuxottica
Francesca Palermo, Research Principal Investigator at EssilorLuxottica, presents the “Enabling Ego Vision Applications on Smart Eyewear Devices” tutorial at the May 2025 Embedded Vision Summit. Ego vision technology is revolutionizing the capabilities of smart eyewear, enabling applications that understand user actions, estimate human pose and provide spatial awareness through simultaneous… “Enabling Ego Vision Applications on

LLiMa: SiMa.ai’s Automated Code Generation Framework for LLMs and VLMs for <10W
This blog post was originally published at SiMa.ai’s website. It is reprinted here with the permission of SiMa.ai. In our blog post titled “Implementing Multimodal GenAI Models on Modalix”, we describe how SiMa.ai’s MLSoC Modalix enables Generative AI models to be implemented for Physical AI applications with low latency and low power consumption. We implemented

“Introduction to Deep Learning and Visual AI: Fundamentals and Architectures,” a Presentation from eBay
Mohammad Haghighat, Senior Manager for CoreAI at eBay, presents the “Introduction to Deep Learning and Visual AI: Fundamentals and Architectures” tutorial at the May 2025 Embedded Vision Summit. This talk provides a high-level introduction to artificial intelligence and deep learning, covering the basics of machine learning and the key concepts of deep learning. Haghighat explores

Why Synthetic Data Is Shaping the Future of Computer Vision
This blog post was originally published at Geisel Software’s Symage website. It is reprinted here with the permission of Geisel Software. The future of “seeing” Synthetic data solves data bottlenecks: It reduces the time and cost of collecting and labeling data—particularly rare edge cases—which often consume the majority of AI development time. Complex scenes remain

“Deep Sentinel: Lessons Learned Building, Operating and Scaling an Edge AI Computer Vision Company,” a Presentation from Deep Sentinel
David Selinger, CEO of Deep Sentinel, presents the “Deep Sentinel: Lessons Learned Building, Operating and Scaling an Edge AI Computer Vision Company” tutorial at the May 2025 Embedded Vision Summit. Deep Sentinel’s edge AI security cameras stop some 45,000 crimes per year. Unlike most security camera systems, they don’t just… “Deep Sentinel: Lessons Learned Building,
Automated Driving for All: Snapdragon Ride Pilot System Brings State-of-the-art Safety and Comfort Features to Drivers Across the Globe
This blog post was originally published at Qualcomm’s website. It is reprinted here with the permission of Qualcomm. Qualcomm Technologies, Inc. introduces Snapdragon Ride Pilot at IAA Mobility 2025 What you should know: Qualcomm Technologies, Inc. has introduced Snapdragon Ride Pilot to help make driving more safety-focused and convenient for people around the world. Features

“Introduction to Knowledge Distillation: Smaller, Smarter AI Models for the Edge,” a Presentation from Deep Sentinel
David Selinger, CEO of Deep Sentinel, presents the “Introduction to Knowledge Distillation: Smaller, Smarter AI Models for the Edge” tutorial at the May 2025 Embedded Vision Summit. As edge computing demands smaller, more efficient models, knowledge distillation emerges as a key approach to model compression. In this presentation, Selinger delves… “Introduction to Knowledge Distillation: Smaller,

